NVMe lifespan : How long can I expect an M2 NVMe PCIe SSD to last: Basically your SSD will die approx in 10 Years and can also die more soon it totally depends on your usage if you write a lot of data on SSD on daily basis then ya it shall die within 1–2 years and to calculate here’s the formula:-
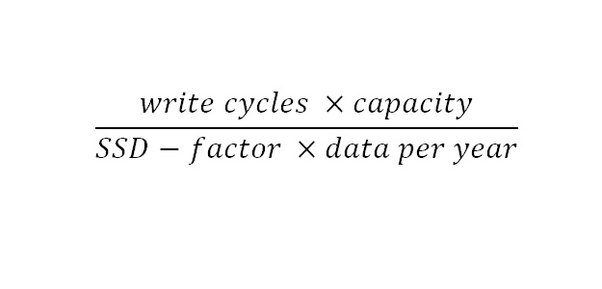
how long will data last on ssd
after completion of the write cycle, SSD will stop writing data and given a chance to copy files and after that, you need to replace it with new SSD.
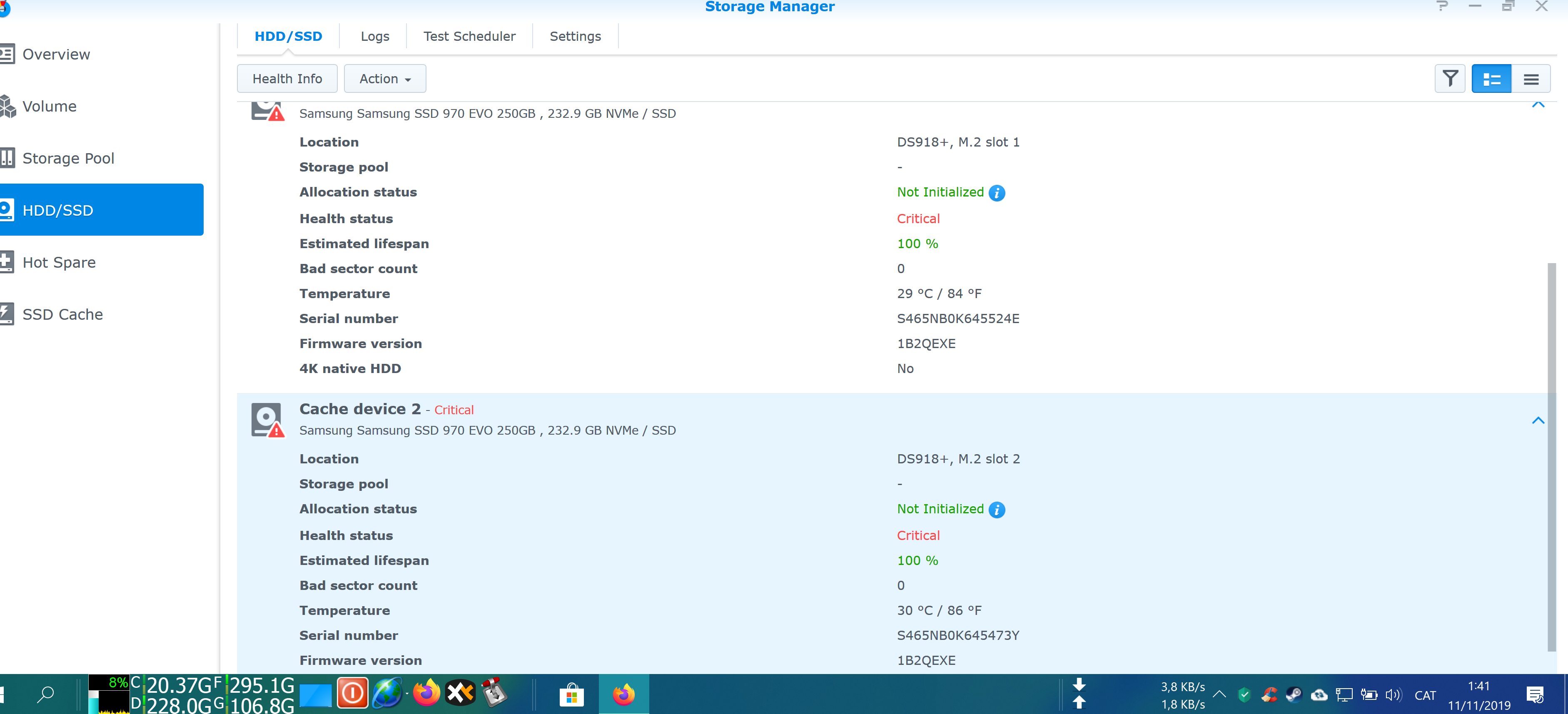
This depends on FLASH used, controller, SSD size and usage. Also temperature.
Let’s start with FLASH types and some drives:
- Samsung 970 Pro – MLC and 1200 TBW for 1TB
- Samsung 860 EVO – TCL and 600 TBW for 1TB (1200 for 2TB)
- Samsung 860 QVO – QLC and 360 TBW for 1TB
- Samsung 980 Pro – TCL and 600 TBW
But there are drives with very low TBW, cheaper drives, usually without DRAM. Eg Crucial BX500 has only 240 TBW in 960GB and 360 TBW for 1TB model!
Above times are also tied to 3 or 5 years warranty. Let say in 1200 TBW and 3 year warranty something is wrong.
To understand why is so you need to know how FLASH works. I will go in short here. FLASH stores bits into “floating gates”, consider it as water in closed bottle. Bits could be written but not changed (1 -> 0 or 0 -> 1). Change requires erase and erase is big problem. Erase is performed in blocks, usually 4kB in size (that’s reason why SSDs have 4kB clusters). Btw writes are also not performed on bits, nor even bytes but pages of many bytes (usually less then erase page).
Increase of capacity is related to number of bits stored in each cell (floating gate). MLC stores 2 bits, TCL 3 and QLC 4 bits per cell. Think of this as level of water in bottle.
Every write and especially erase “soften” material around gate (let say soften bottle glass) and leaves some water in bottle. With time it is not possible to know what is written (especially with TLC and QLC).
And this is problem cause every write, eg temporary file, requires erase. Bigger drive – more sectors to choose from!
Controller is important for endurance but it has limits. Problem is when drive gets full. Degradation begins and accelerates after 75% or so. There are not enough free sectors and only thing what controller could do is to move stored data around. But, this has problems and limitations.
To conclude. Bigger drive is much better! It is faster and will last longer. Most drives today have similar prices. Choose one with 5 years warranty and higher TBW. 240 TBW might look a lot but it is not so much. Of course, depends what you are doing.
If you choose PCIe-4 drive ensure good cooling! Any SSD needs cooling what is a bit problem for NVMe – usually not in air flow. That’s reason why most PCIe-4 drives have coolers on top. After some 60 deg Celsius degradation increases!
TBW specified above is for 40 deg! For example at 80 deg drive could be killed in few days (constant writing).
Today we have a lot of SSDs older than 8 years and there are not so many problems. But, all older drives were SLC or MLC. TLC was launched in 2010.
Google for Backblaze, they have nice statistics.
If you believe the shit the manufacturers publish, the average is about 1,000,000 hours MTBF.
Realistically speaking, if it survives the first 30 days or so, it’ll likely last as few years.
So how long will an NVMe drive last?
- Some NVMe models on the market claim a guaranteed lifespan of 800TB for their 1TB model and 1200TB for their 2TB model. They also claim 1.5 million hours of the mean time between failures and back it up with a five-year warranty.
- If you’re looking for long-lasting performance from your storage drives, NVMe is the future, and you should be exploring how you can integrate them into your current storage solution.
- These drives are designed to replace the SATA technology with the higher bandwidth PCIe technology. This upgrade can result in 4x read/write speeds and 10x seek rates than a SATA drive.